What is your core muscle group and how does it work? Practically every fitness program known to humanity talks at some point about “core muscles” and how to strengthen them. But what are your core muscles? Meet the team of muscles that works together to create mobility and stability throughout your body.
A lot of programs focus on the rectus abdominus muscles (known as the six-pack) but the six-pack is really just a supporting player.
The core muscles aren’t just on the front of your body. They make up a shape like a soup can with a top, sides, and bottom. The core muscles are constantly in dynamic interaction to provide both support and movement to your torso and internal organs and control how you breath, use the bathroom, have sex, digest food, and much more. They need to be trained together so that they can coordinate for both strength and flexibility.

Core Muscle group is like a soup can in the middle of the body
What is Your “Core Muscle” Group?
The Diaphragm
The diaphragm is the top of the soup can, a big dome of muscle at the bottom of the rib cage. It attaches to our spine, rib cage, and the muscles all around our midsection, with holes in it where the aorta, vena cava, and esophagus pass through on their way to the lower body.

The diaphragm muscle
The primary job of the diaphragm is breathing. When it contracts, the dome drops down pulling air into the lungs. When it relaxes it lifts back up into its original dome shape as the lungs empty out. Having the ability to fully relax and contract the diaphragm is very important for taking full, deep breaths. This is called diaphragmatic breathing, not because it only uses the diaphragm (other muscles also play important roles) but because it makes full use of the diaphragm.
The diaphragm also works with the rest of the core muscle team to stabilize the upper body. When other core muscles aren’t working well the diaphragm ends up needing to work overtime as a stabilizer, making it hard to relax. This can have a big effect on important stuff like your breathing patterns and neck and back flexibility.
The Transversus Abdominus
While the six-pack muscle is the showboater of the core muscle group, the transversus abdominus is the real power behind the throne. This is the deepest of the three muscles I like to call the “meat corset” because they wrap around our waist and, when they contract, they squeeze in to stabilize us from all sides. The meat corset makes up the sides of the soup can.
The TA attaches in back near your spine and wraps all the way around your waist where it comes together at a thin line of connective tissue in the middle of your belly. A happy TA works together with the other meat corset muscles as a primary stabilizer for the spine and entire upper body.
The Internal and External Obliques
The obliques are the second and third layer of the famous meat corset. They wrap around your waist over the TA at slight angles, providing even more stability and adding a dynamic side-bending and twisting ability that gives our spine it’s famous mobility.
The meat corset muscles work in constant coordination with the diaphragm so that when the diaphragm relaxes and you exhale the meat corset ramps up to take over most of the job of holding you up. If the meat corset is sleepy and uncoordinated then the diaphragm doesn’t get to relax and you can end up with breathing issues, back and neck pain, poor posture, stiff spine, and a long list of additional issues.
Check out the work of the Postural Restoration Institute if you want to do a deep dive here.
The Pelvic Floor
The pelvic floor muscles are a basket of interwoven muscle fibers that sits at the base of your pelvis. They are the bottom of the soup can.
The two main muscles are the levator ani and the coccygeus, that support your internal organs and have little holes in them to control your poop and pee, and the opening of the vaginal canal if you are AFAB (assigned female at birth).
The pelvic floor muscles are part of the intricate choreography of the soup can. When the choreography is off the pelvic floor can become sleepy and under-working, or stressed out and over-working, which can have unpleasant repercussions for digestion, pooping and peeing, and sex.
The Erector Spinae
The erector spinae are a bunch of small muscles that stick out all along your spine like little pine tree branches, connecting the vertebrae together. They are the solid seam in the side of the soup can that provides extra stability and helps to keep your body upright but mobile. If the rest of the soup can gets sleepy and squishy the erector spinae can end up very over-worked and tight. Unpleasant outcomes include tight back muscles, back spasms, and even displacement of the vertebrae.
The Rectus Abdominus
Here we have arrived at the six-pack, all the way down at the bottom of the list. The rectus abdominus attaches to the bottom front of the rib cage and the top front of the pelvis. It’s sole job is to forward flex the spine (like in a sit-up) but it isn’t really awesome at stabilization. It’s a bit of a one-trick pony: very good at an important job but not good at anything else.
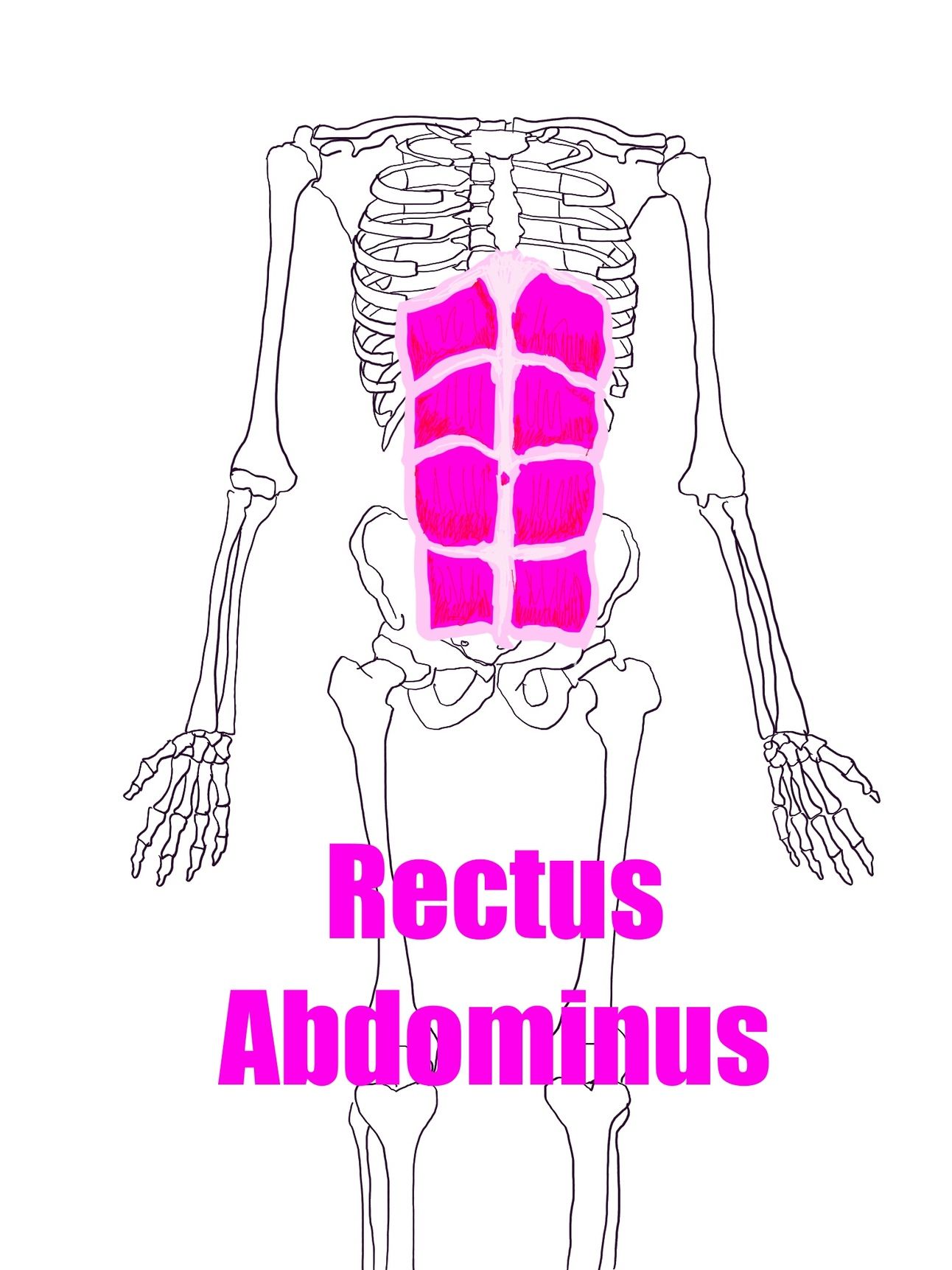
Rectus Abdominus
When the soup can is squashy the rec abs can end up over-working. You can tell if you have too much rec ab in your life if, when you try to do a sit-up, your abs push out instead of in. This ultimately robs you of a lot of your strength and stability.
Honorable mention goes to the Iliopsoas
Even though it isn’t technically part of the soup can, you can’t talk about core muscles without mentioning the iliopsoas. This is a loving union of two muscles, the iliacus and the psoas, that attach to the spine at the same place as the diaphragm and swoop down inside your body, through the pelvic floor, to attach to your upper inner thigh. I have a lot of content on the iliopsoas and how to fall in love with yours, so I wont get into too much detail here.
Key Takeaway about the Core Muscle Group and How it Works
The most important thing to remember about the core muscle group and how it works, is that these muscles all work together and what affects one of them, affects all of them.
The core muscles are always moving because you are always breathing and breath is the first and most accessible way to start to feel how they work and interact. Coming soon is a series of workouts and tutorials on how to coordinate and strengthen your core muscle group so that they work together as one happy team!
Happy Bendings!Kristina
The post What is your “Core Muscle” Group and How Does it Work? appeared first on Fit & Bendy.

